Samsung SSD 750 EVO 120GB and 250GB Review
IOMeter Sequential Performance
Starting in 2015 Legit Reviews brought back synthetic IOMeter v1.1.0 testing to our high-end Solid-State Drive reviews as we feel that the canned benchmarks no longer show enough of the performance picture nor do they expose many of the heat issues that we are starting to encounter on M.2 PCIe SSDs. We start out testing each drive with IOMeter, but first we prepare the drive. This is done by using Parted Magic to complete a full Secure Erase each and every drive. Next we use IOMeter to prefill the drive by performing the industry standard 128KB, aligned, sequential write workload across the entire drive for a period of 20 minutes. Once the drive is conditioned we run our saved sequential test profile that runs our 128KB test for one minute without any idle time in between the tests. The queue depth is set to 32 as we feel with NVMe drives starting to come out that we need to increase our IO depth.
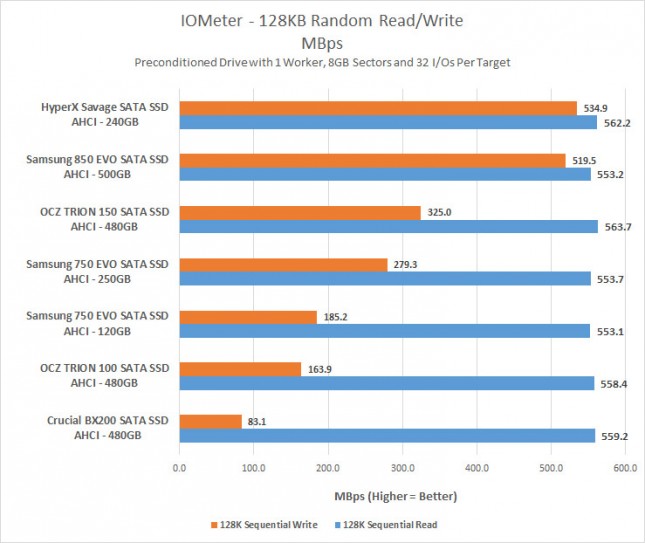
The 128KB Sequential Read/Write test is done primarily to make sure the drives we are testing meet or surpass the manufacturer specifications for sequential Read/Write performance. The Samsung SSD 750 EVO Drives both topped out at 553 MB/s, but the write speeds of each drive were lower than one might expect. We topped out at 280MB/s on the Samsung SSD 750 EVO 250GB and 185MB/s on the Samsung SSD 750 EVO 120GB.
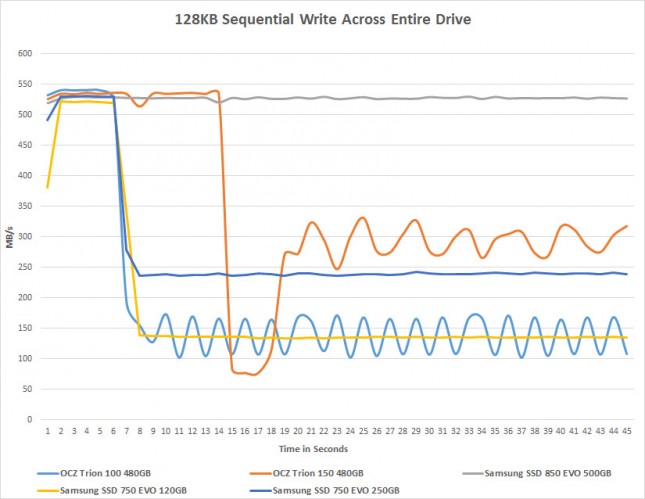
This is happening because the drives cache is filling up. The chart above shows what happens to some TLC drives with the write buffer fills up after a number of seconds. Short benchmarks don’t show this performance drop, but when you do long sustained writes you’ll see it. Both the Samsung SSD 750 EVO 120GB & 250GB drives have their performance significantly drop off after about 7 seconds of continual writes. What we found was interesting is that the 750 EVO 120GB drives performance dropped to roughly 133-136MB/s after the cache was full whereas the 750 EVO 250GB dropped to down to the 236-241 MB/s range. This is likely due to the number of NAND Flash lanes available to the controller as the 750 EVO 120GB SSD has one TLC NAND Flash chip versus the two used on the 750 EVO 250GB SSD. The Samsung SSD 850 EVO 500 GB drive doesn’t have a performance drop off like the other TLC drives, but keep in mind that it has 512MB of DDR3 cache versus the 256MB on the 750 EVO series and has one extra controller processor enabled.
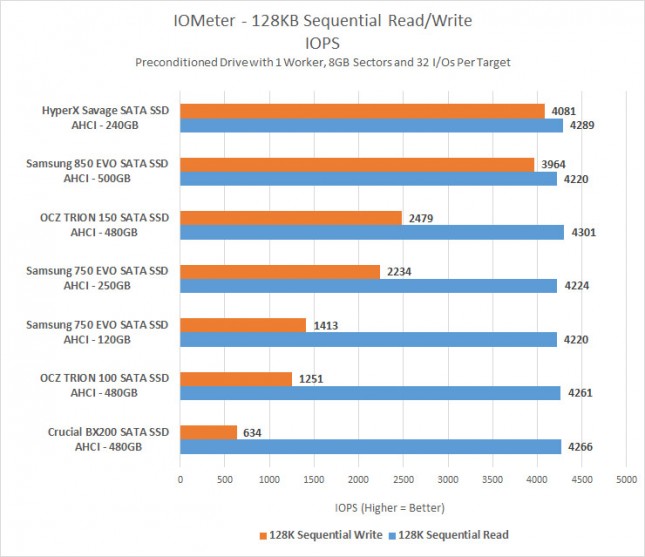
For those that like to know the IOPS results you are looking at around 4,220 IOPS for the sequential read on both drives. The Samsung 750 EVO 120GB averaged 1413 IOPS on the sequential write and the 250GB version of the drive averaged 2234 IOPS.
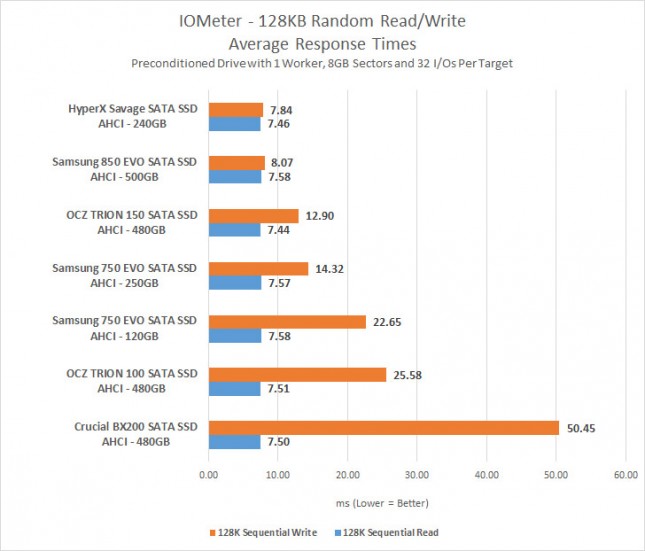
Having high IOPs per second is generally considered good, but you also look at the latency when interpreting the results. Just because the IOPs are high it might not mean that the data is being delivered at a reasonable latency and this could cause for a poor user experience. Both 750 EVO drives had around 7.5ms response times on the read operations, but you can see there was an 8ms difference on write operations!