Intel SSD 600p Series 512GB NVMe SSD Review
Taking A Look At Sustained Write Performance

Triple-Level Cell TLC NAND based SSDs perform usually quite well, but when you copy a large amount of data to the drive without and idle time you’ll often find a large drop in write speed. TLC NAND is great in applications where write operations are limited , but is usually not recommended for critical systems that have heavy write operations as they have lower endurance ratings than SLC or MLC NAND and of course sustained write performance isn’t stellar. In recent years drive manufactures have been figured out that by using SLC or TLC treated as SLC as a cache they can keep the drives overall write performance high as long as the amount of data being written to the drive fits in the cache. If you overflow the cache, you are then writing directly to the TLC NAND and the write performance will drop down to that level. It should be noted that the SLC cache will clear once the drive idles, so this only impacts long writes that are many GB in size. This might not be a typical workload scenario for this ultra-value or mainstream drives, but still something worth pointing out!
Let’s take a look at the Intel SSD 600p Series 512GB drive to see how it handles sustained write scenarios.
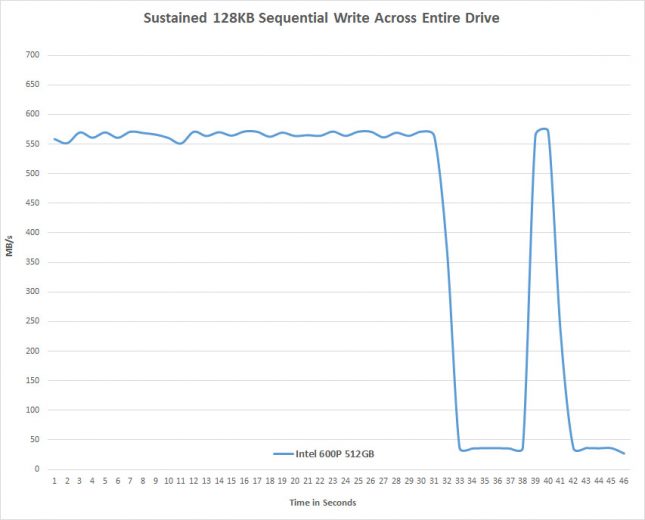
The 600p starts out at around 550 MB/s sequential write speeds, but after 31 seconds (17.5GB of writes) the performance dropped down to nearly 30 MB/s before recovering and then dropping again. When you average the test results over the 45 second period that we are focusing on these are the average speeds that you come up with:
- Patriot Hellfire M.2 480GB – 1226.38 MB/s
- Samsung SSD 960 EVO 1TB – 1223.07 MB/s
- Samsung SSD 850 EVO 500GB 527.23 MB/s
- Crucial MX300 750GB SSD 522.4 MB/s
- ADATA SU800 512GB SSD 520.85 MB/s
- Toshiba OCZ VX500 512GB SSD 520.41 MB/s
- Intel 600p 512GB – 427.295 MB/s
- Toshiba OCZ Trion 150 480GB 347.75 MB/s
- Samsung SSD 960 EVO 250GB – 326.37 MB/s
- WD Blue SSD 1TB 314.81 MB/s
- Kingston UV400 480GB 267.04 MB/s
- OCZ Trion 100 480GB 192.19 MB/s
- ADATA SP550 480GB SSD 103.53 MB/s
The Intel SSD 600p 512GB drive performs no better than most SATA III SSDs with regards to long sustained writes as it averaged just 427 MB/s over our short 45 second long test.
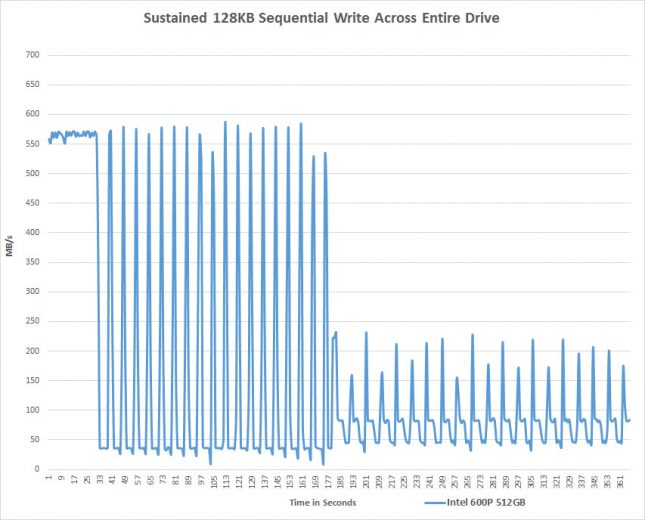
When you stretch this test out for a period of six minutes you’ll see a pattern develop and performance never fully recovers as the drive isn’t given the opportunity to take a break for the cache to clear and to be able to run the TRIM and garbage collection algorithms. Once the SLC cache has been filled on the 600p the write performance slows to a crawl and you get spike of performance and then write latencies as the dual-core controller struggles to keep up. This is due to the fact that Intel doesn’t allow the data to bypass the cache and be written directly to the TLC NAND Flash like some other solutions on the market. All the data must go must go through the cache before being written and that is too much for this controller to handle.
Let’s take a look at some common benchmarks!