Crucial P2 250GB and 500GB SSD Review
ATTO & CrystalDiskMark
ATTO v4.01.0f1
ATTO is one of the oldest drive benchmarks still being used today and is still very relevant in the SSD world. ATTO measures transfers across a specific volume length. It measures raw transfer rates for both reads and writes and places the data into graphs that can be very easily interpreted. The test was run with the default runs of 0.5KB through 64MB transfer sizes with the total length being 256MB.
ATTO Disk Benchmark:
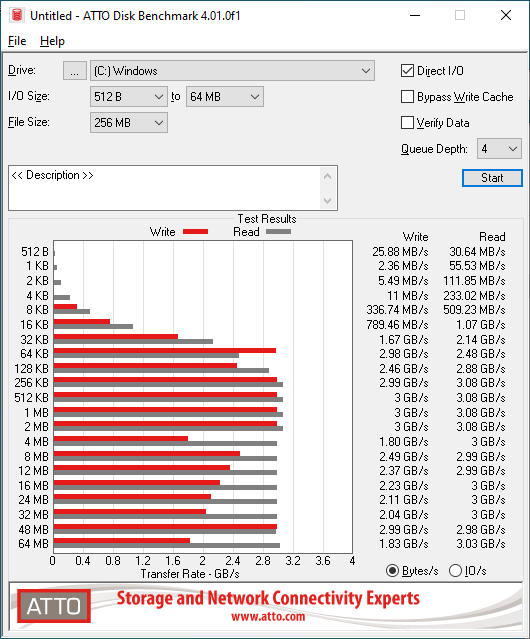
Crucial P2 250GB:
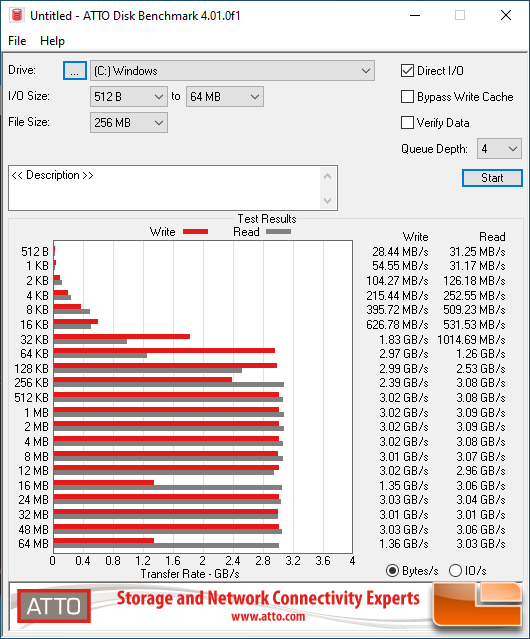
Crucial P2 500GB:
Benchmark Results: On ATTO Disk Benchmark we see the Crucial P2 250GB & 500GB drives coming in with some really crazy good benchmark results as the P2 500GB drive manages to best 3GB/s for both the sequential read and write test. Phison has been optimizing their controller firmware to better handle compressible 0-fill data for some time and it looks like they have done it so well that they are rendering some benchmarks like this one useless for real-world testing.
CrystalDiskMark 7.0.0 x64
CrystalDiskMark is a small benchmark utility for drives and enables rapid measurement of sequential and random read/write speeds. Note that CDM only supports Native Command Queuing (NCQ) with a queue depth of 32 (as noted) and shows the highest score of five runs.
CystalDiskMark:
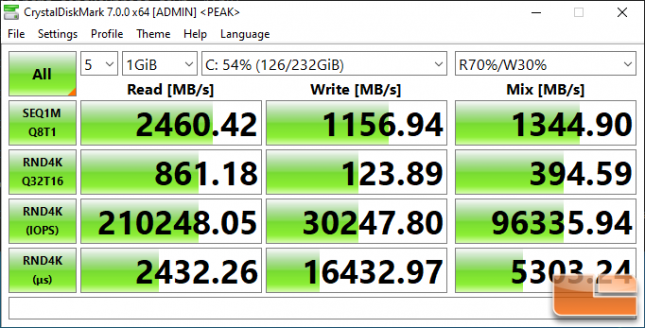
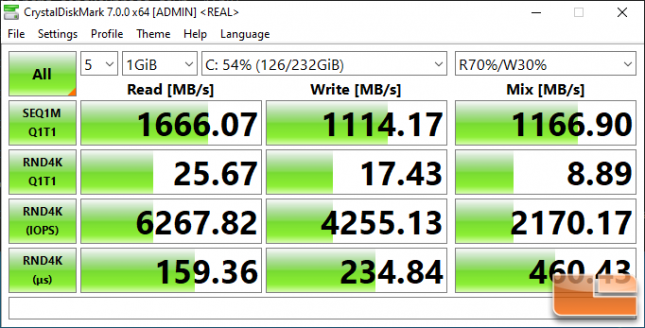
Crucial P2 250GB:
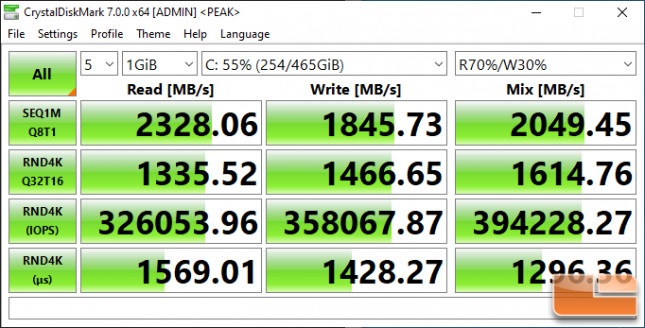
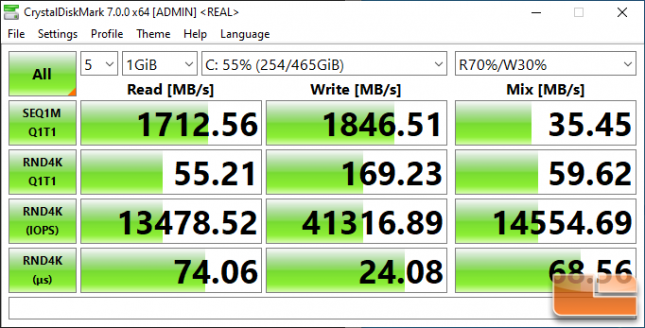
Crucial P2 500GB:
Benchmark Results: The Crucial P2 250GB drive topped out at 2,460 MB/s read and 1,157 MB/s write on the sequential test at QD8. This drive is only rated to hit 2,100 MB/s read and 1150 MB/s write, so it is exciting to see both of these ratings bested on our AMD Ryzen 5 3600X CPU on an AMD X570 powered board.
The larger Crucial P2 500GB drive managed to reach 2,328 MB/s read and 1,846 MB/s write. This 500GB capacity model is rated at 2,300 MB/s read and just 940 MB/s write. We are able to do just better on the sequential read side, but are nearly doubling the performance on the sequential write side.
That said, remember the Crucial P2 500GB drives being tested is using TLC NAND and not the QLC NAND that the speed ratings are based off of.
Let’s look at some other benchmarks!