ASUS GeForce GTX 590 3GB Video Card Review
The ASUS GTX590 3074MB Video Card

The card that we are looking at today is the ASUS ENGTX590/3DIS/3GD5 video card! This card is technically overclocked as it comes with a GPU core clock speed of 613MHz, which is slightly higher than the NVIDIA reference design core clock of 1607MHz.
| Core Clock | Shader Clock | Memory Clock | Shaders | MSRP | |
| NVIDIA GeForce GTX 590 | 607MHz | 1215MHz | 855MHz | 1024 | $699.99 |
| ASUS GeForce GTX 590 | 613MHz | 1225MHz | 855MHz | 1024 | $699.99 |
ASUS is using the NVIDIA reference designed PCB and GPU cooler on their GTX 590 video card, so the only real difference is the 6MHz faster core clock speed. ASUS isn’t charging for this slight overclock, though, as the price of the card is still $699.99.

The ASUS GeForce GTX 590 rocks a black and green color scheme and with a large center mounted 90mm cooling fan. This fan design exhausts most of the hot air
from the inside of
your case out, but the card does have some exhaust vents on the top and the right side of the card is open.
When it comes to dimension the PCB is 11.5″ x 4.5″ in length and height. This makes the NVIDIA GeForce GTX 590 slightly shorter than the AMD Radeon HD 6990 as that card is 12″ long with the stock fan shroud.

Flipping the ASUS GeForce GTX 590 video card over we can see that NVIDIA has a pair of back plates covering both of the GPU’s. Rather than using Philips screws on these covers they are held down by Torx screws (T10).

The ASUS Ultimate GeForce GTX 590 Ti 1GB GDDR5 graphics card has three dual-link DVI-I outputs and one that is mini DisplayPort compatible. NVIDIA clearly designed this card to easily work with a 3D Vision Surround setup using DVI connections.
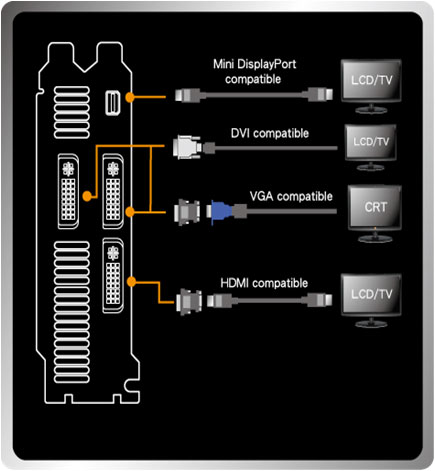
The above illustration will give visual learners a better idea of how the connectors work. (If you look at the illustration closely, though, you’ll notice they have the exhaust bracket flipped wrong.)

The ASUS GeForce GTX 590 3GB video card requires a 700 Watt or greater power supply with a minimum of 50 Amps on the +12 volt rail. It also requires that the power supply has two 8-pin PCI Express power connectors for proper operation. It should be noted that the NVIDIA minimum system power requirement is based on a PC configured with an Intel Core i7 3.2GHz CPU. If you want to run SLI we have been told that a 11000 Watt or greater power supply is suggested by NVIDIA. NVIDIA refuses to give +12V rail Amp requirements for SLI, which is strange since they suggest them for single card solutions.

The GeForce GTX 590 graphics card does support
Quad-SLI and has a single SLI bridge located along the top edge of the
graphics card. What is nice about this card is that you don’t need to buy another one to run 3D Vision Surround. You can hook up three monitors to this card’s three dual-link DVI outputs and game in 3D across all the monitors if you wanted to.

NVIDIA included a small LED light behind their logo on the top of the card, which makes it stand out if you have a case window on your PC. NVIDIA says that this light will flash if your power supply isn’t up to snuff, so it does serve a purpose. (You need power to turn a light on right – sigh) You can unplug the 2-pin wire for the LED light if you don’t want it to be on though, which is a nice touch as we have seen some LED lights get placed on the PCB and you can’t easily turn them on or off.

To unplug the light you need to remove the fan cover like we did above. This takes a few minutes and you just need to remove six Philips screws and unlock the plastic fan shroud. This is also the same thing you’d need to do if you wanted to clean out the cooling fins on the heat sink if they ever get dusty and dirty.
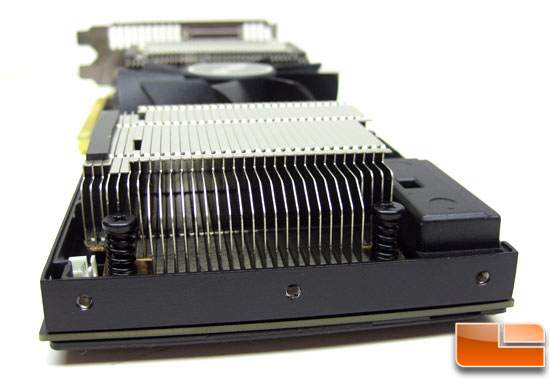
The GPU coolers used on each of the GF110 Fermi GPUs look to have copper base plates with aluminum cooling fins that are pretty thin and placed close together.

We didn’t want to take apart our only card just yet, so here is an image of the GeForce GTX590 without the GPU cooler on it. NVIDIA said that a 12-layer PCB is used. To help disperse heat more effectively across the PCB, two ounces of copper are used for each of the boards power and ground layers on the PCB. This also enhances the boards longevity.
Powering the twin GPUs is a 10-phase advanced digital power controller with over-voltaging capability, while two dual-phase controllers provide power for the boards GDDR5 memories. For maximum cooling performance, the cooling subsystem of the GTX 590 consists of two self-contained GPU coolers, each utilizing a copper vapor chamber and dual-slot heatsink.
To help provide cooling for the PCB and its components, an aluminum baseplate is secured to the top of the board. In addition, two backplates are mounted on the bottom of the board to cool the graphics memory.

Comments are closed.