AMD Ryzen 7 2700 8-Core 65W Processor Review
Power Consumption, Performance Per Watt/Dollar
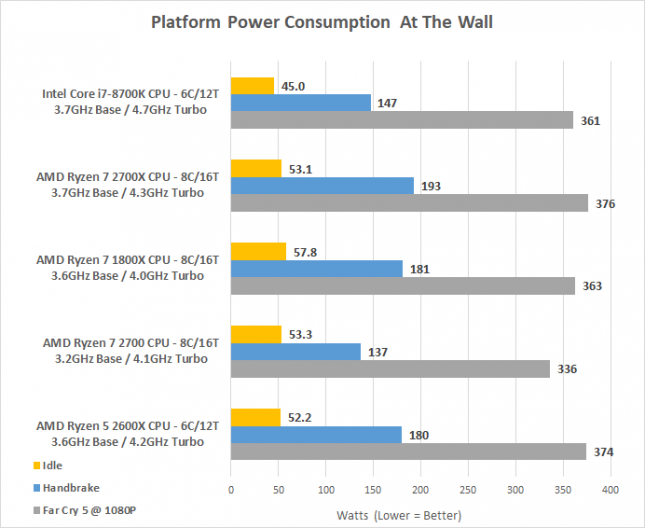
Power consumption is something that you should be aware of with regards to processors as someone is going to be paying the electric bill. The AMD Ryzen 2000 series ranges between 65W and 105W TDP, which is a fairly wide power range. The models without XFR 2 technology are both 65W TDP parts that that means the Ryzen 7 2700 that we are reviewing today has a TDP rating of 65 Watts, which is 38% less than the 2700X.
- AMD Ryzen 7 2700X – 105W TDP
- AMD Ryzen 7 2700 – 65W TDP
- AMD Ryzen 5 2600X – 95W TDP
- AMD Ryzen 5 2600 – 65W TDP
Our testing shows that AMD Ryzen 7 2700 uses about the same power as a 2600X or 2700X processor at idle. When running a multi-threaded CPU workload like Handbrake. On Handbrake the Ryzen 7 2700 used 29% less power than the Ryzen 7 2700X. While gaming there was an overall system power decrease of about 12%. So, idle power is the same as any other Ryzen 2000 series part and at load it uses less power than the XFR 2 supporting models. These are pretty solid power numbers!
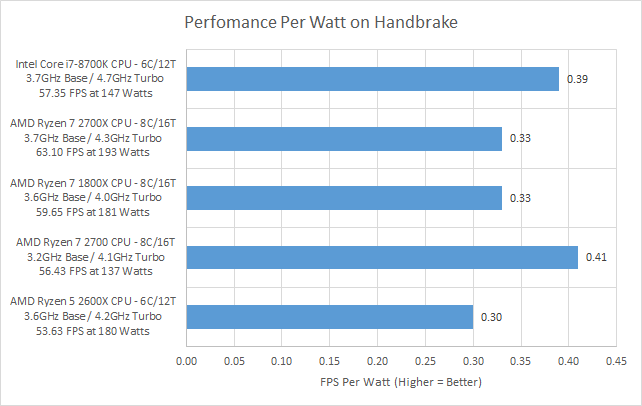
In fact if you look at performance per Watt the AMD Ryzen 7 2700 does better than the four other processors we are comparing it to, so from a power efficiency point of view it does really well. We are using Handbrake for our example here as most desktop users these days do some video editing.
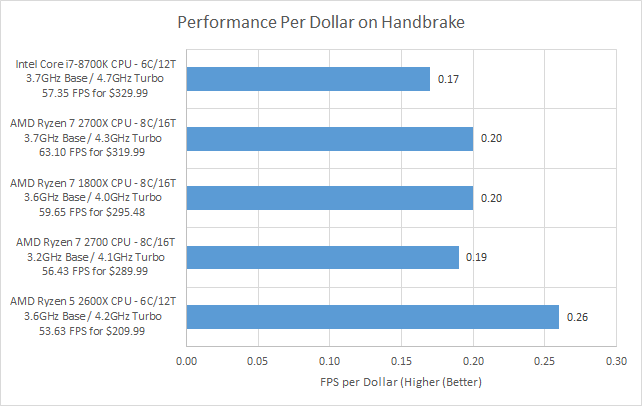
When you look at how much each FPS is costing on Handbrake, though the AMD Ryzen 7 2700 has the highest cost of the four Ryzen processors tested.
Another way of looking at this would be performance per dollar and the results are the same. The AMD Ryzen 5 2600X offers the best performance for the dollar spent by a good margin.
So, you the Ryzen 7 2700 has good performance per watt, but the performance per dollar could certainly be better.
Let’s take a look at overclocking!