Intel CPU Bug Could Bring Massive Performance Hit In Some Applications
A ‘fundamental design flaw’ has been discovered in multiple generations of Intel processors that are only fixed by a significant redesign of Windows and Linux kernels. The design flaw creates a security vulnerability in Intel CPUs and it appears that AMD is not impacted. The scope of this flaw is huge as it is rumored to impact all Intel processors dating back at least a decade. Some Linux patches have already been distributed and Microsoft is expected to address the bug in Windows on one of its monthly Patch Tuesday update. Patch Tuesday typically occurs on the second, and sometimes fourth, Tuesday of each month in North America. The specifics of the exploit are currently under embargo, but details are starting come out thanks to coverage by The Register, Python Sweetness and Phoronix.
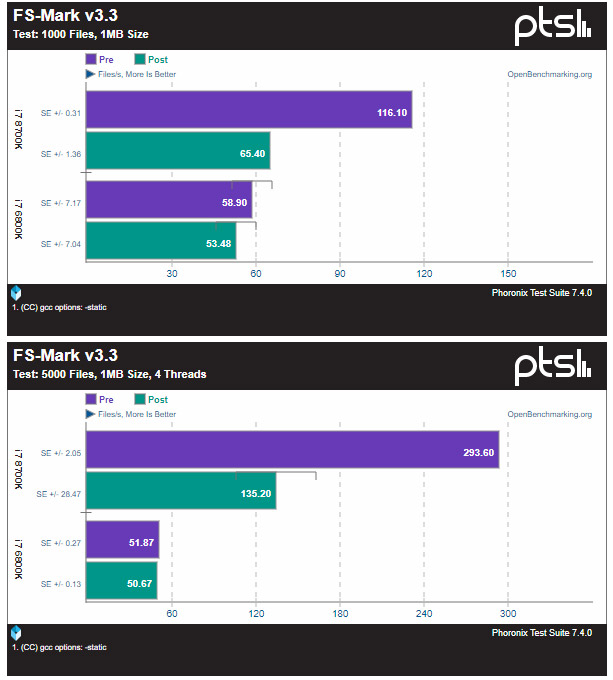
From what we gather the bug allows programs run on an impacted system to to “illegally” access certain contents in protected kernel memory. This is the place where your super-secure things like passwords and log-ins reside. The kernel “fix” appears to be the implementation of Kernel Page Table Isolation (PTI) that makes the kernel invisible to running processes. The bad news is this solution has some sites reporting a performance drop of 5-30% on many applications with some taking an even larger performance hit. It should be noted that all performance tests thus far have been run on Linux. Michael Larabel over at Phoronix has already tested the new OS-level patch for Linux an an Intel Core i7-8700K and Intel Core i7-6800K processor and noticed some pretty big differences in some benchmarks.
AMD processors are not impacted according to The Register, so recent AMD Ryzen, Threadripper and EPYC CPU don’t have any security issues to worry about. The bad news is that the Linux patch that has been rolled out it being applied to both AMD and Intel processors. AMD says to not enable the PTI patch on AMD processors by disabling the page table isolation setting that is on by default. Hopefully there will be a way to disable this on Windows or maybe it won’t be rolled out to all x86 processors.
AMD processors are not subject to the types of attacks that the kernel page table isolation feature protects against. The AMD microarchitecture does not allow memory references, including speculative references, that access higher privileged data when running in a lesser privileged mode when that access would result in a page fault. – The Register
The good news is that the testing Michael Larabel did on an Intel Core i7-8700K processor on Linux with the latest kernel Git code did not sow any major negative performance impacts on the gaming side. The benchmarks were run on game titles like CS:GO, Deus Ex: Mankind Divided, Dota 2, Dawn of War III, F1 2017, and The Talos Principle. That is exciting news for the gaming community and hopefully it carries over to the Microsoft Windows side!

In other news, both Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services have scheduled maintenance that will take place over the next week, although there is no detailed explanation for the downtime, but it is likely due to this bug. This is going to impact millions of people and all businesses, so be sure to keep an eye on this if you work in the IT department!
It appears that this security bug will likely lead to Intel CPU architecture changes that are needed to improve how virtual memory is handled. Could this delay next-generation products? It is too early to tell, but this looks like it could be as big as the infamous Pentium F00F bug.
Update: Some Microsoft Windows performance numbers have started to come out and the performance impact doesn’t appear to be big on the applications this site tested They only used an Intel Core i7-7700K, so testing is limited so far.