Intel SSD 600p Series 512GB NVMe SSD Review
Intel SSD 600p Series – NVMe At Entry-Level M.2 PCIe Price Points
If you are looking for a low cost M.2 NVMe drive for your desktop PC or laptop you are looking at the right review. Intel recently released the SSD 600P Series drives that use the M.2 2280 PCIe 3 x4 (single-sided) interface and is one of the very first NVMe drives to feature 3D TLC NAND Flash memory. Intel went with the Silicon Motion SM2260 controller on this particular series and pair it with Intel 384Gb 32-layer 3D TLC NAND Flash memory. The result was an affordable client storage drive series that Intel hopes will lure some people away from the high-end SATA III SSD market and over to PCIe M.2 segment. With pricing starting at just $55.99 for a 128GB drive ($0.44 per GB) and topping out at $289.99 for the 1TB drive ($0.28 per GB), the Intel SSD 600p series might do just that. The sweet spot for the SSD market would be the 256GB and 512GB capacities and the Intel SSD 600p Series has you covered as the 256GB model is priced at $79.99 ($0.31 per GB) and the 512GB model at $170.00 ($0.33 per GB) isn’t too much more.

Intel SSD 600p Series Features:
- Form Factor: Single-Sided M.2 2280
- Interface: PCIe 3.0 x4
- Capacities (GB): 128, 256, 512, 1024
- Controller: Silicon Motion SM2260
- NAND: Intel 384Gb 32-layer 3D TLC
- SLC Cache: Up to 32GB
- AES 256-bit self-encryption
- MTBF: 1,600,000 hours
- Sequential Read: Up to 1800 MB/s
- Sequential Write: Up to 560 MB/s
- 4K Random Read: Up to 155K
- 4K Random Write: Up to 128K
- Power Consumption (Typical):
- Active: 100 mW
- Idle: 40 mW
- L1.2 Sleep: 5 mW
- Warranty: 5-Years
The Intel SSD 600p is offered in four capacities;128GB, 256GB, 512GB and 1TB, but a 2TB version is possible if there is enough demand for Intel to bring one to market. All of the drives use the M.2 2280 (80mm) form factor and are single-sided, meaning they are able to work in desktops and laptops with ease. Like most all SSDs, performance greatly varies depending on the capacity. The Intel SSD 600p 128GB drive is the slowest with up to 770 MB/s sequential reads and 450 MB/s sequential writes, while the Intel SSD 600p 1TB drive goes up to 1,800 MB/s sequential rad and 560 MB/s sequential write. Random read and write input/output operations (IOPS) are rated at up to 155K and 128K, respectively. The SLC cache buffer is also difference for each drive with the 128GB having just 4GB of SLC buffer, while the larger 1TB drive has 32GB of SLC buffer. This is the amount of TLC NAND Flash that is operating in SLC mode and helps performance during periods of long sustained writes. If you write enough data and fill up the cache, you’ll be writing data directly to the TLC NAND Flash and will take a massive performance hit. You have to throw a good bit of data at the drive to overflow the buffer though, so it doesn’t happen too often in the real world doing normal mainstream computing tasks.
| Capacity | Sequential Read (MB/s) |
Sequential Write (MB/s) |
Random Read (IOPS) |
Random Write (IOPS) |
SLC Buffer (GB) |
Endurance (TBW) |
| 128 GB | 770 | 450 | 35,000 | 91,000 | 4 | 72 |
| 256 GB | 1,570 | 540 | 71,000 | 112,000 | 8.5 | 144 |
| 512 GB | 1,775 | 560 | 128,500 | 128,000 | 17 | 288 |
| 1024 GB | 1,800 | 560 | 155,000 | 128,000 | 32 | 576 |
Intel has placed a solid 5-year limited warranty on the 600p series and has given them a pretty decent endurance rating. The Intel SSD 600p 128GB is rated at 72 TBW and then that goes up to 144 TBW on the 256GB drive, 288 TBW on the 512GB drive and finally 576 TBW on the 1TB model. The Intel SSD 600p Series has great TBW ratings though as the Intel 600p 1TB drive has a 576 TBW rating and that crushed the 400 TBW rating on the Samsung SSD 960 EVO 1TB drive for example.
| User Capacity (GB) | Raw Capacity (GB) | SLC buffer |
| 128 | 144 = 48×3 | 4GB |
| 256 | 288 = 48×6 | 8.5GB |
| 512 | 576 = 48×12 | 17GB |
| 1024 | 1152 = 48×24 | 32GB |
Once you’ve reached the drives limit you can still continue to use the drive as long as there is enough spare area left to swap out the failed cells in the NAND Flash memory. Once you run out of spare space, the 600p will switch into a locked read-only mode that will allow you to recover your data in a perfect world. Hopefully you backup you data regularly and never have to worry about that years down the road.

Today, we are going to be benchmarking the Intel SSD 600p Series 512GB drive. On the top side of the 600p 512GB drive you’ll find find the Nanya 512MB low-power DDR3 DRAM cache chip, SM2260 eight-channel dual-core controller and three Intel 3D TLC NAND Flash chips.
Flipping the drive over you’ll find no components on the back as this is a single-sided M.2 card.
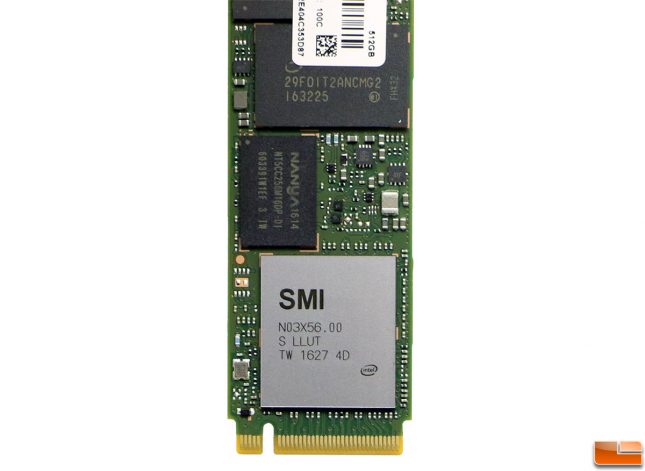

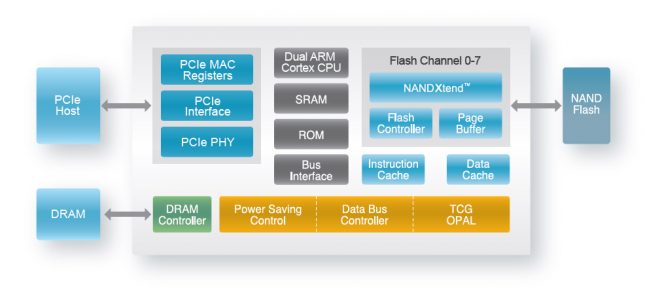
Here is a closer look at the SMI SM2260 controller along with NANYA LPDDR3 DRAM and partially covered Intel 384Gb 32-layer 3D TLC NAND Flash chip. We’ve heard rumors that Intel ‘customized’ the SM2260 slightly for this application and that is why the Intel logo is on the controller. Actually, that isn’t the top of the controller. That is a thin copper-plate that has a shiny silver finish on the top that helps dissipate heat. Intel and Samsung are both using copper layered ‘stickers’ on their latest M.2 drives to help improve thermal performance.
The SM2260 controller was designed for client and entry level enterprise SSDs and features a PCIe Gen3 x4 (8Gbps) interface with eight NAND channels and support for up to 2TB of NAND Flash memory. This controller is PCIe 3.1 and NVMe 1.2 compliant and supports NANDXtend Technology of LDPC hard and soft decoding as well as RAID protection that together enhance the P/E cycles of 3D NAND.
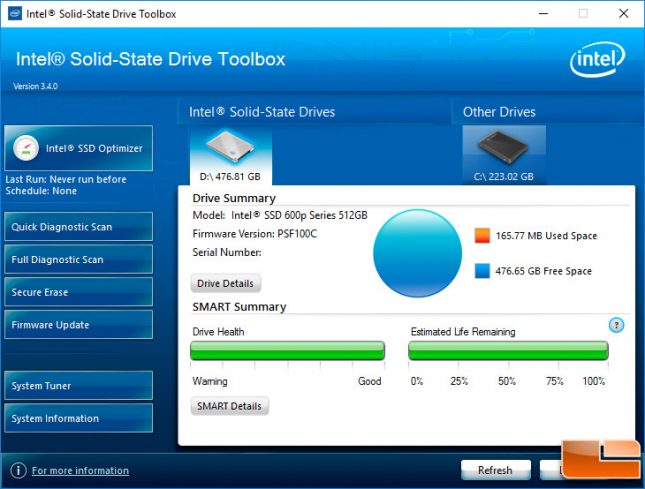
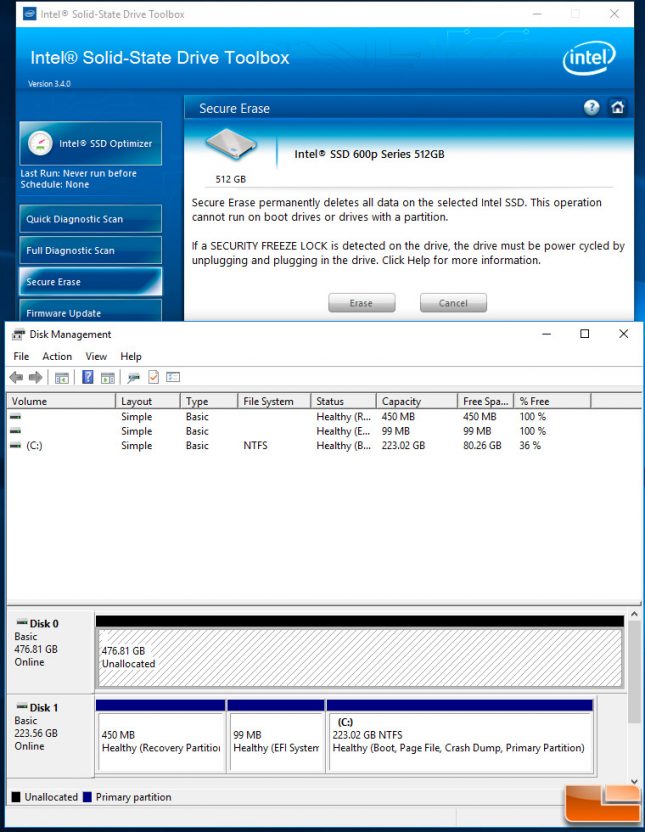
The Intel SSD 600p Series can be used with the Intel SSD Toolbox. This utility will let you check how much of the drives endurance is left, show how much space is being use, the S.M.A.R.T. details, perform a secure erase and even update the firmware.
Unfortunately, even when using the latest Intel SSD Toolbox build (v1.3.4) we were unable to secure erase the Intel SSD 600p series and had to use 3rd party utilities to do that.
Let’s take a look at the test system and then jump into the benchmarks to see how the Intel 600p performs against other M.2 NVMe drives by Samsung, OCZ, Patriot and others.